What are the main HGV regulations I need to be aware of?
Operating HGVs over 7.5 tonnes in the UK requires strict compliance with a range of regulations designed to ensure road safety, vehicle integrity, and responsible operation. Below is a practical summary of the key rules that every driver and operator should understand.
1. Operator Licensing
HGVs over 3.5 tonnes used for business purposes must operate under a valid Operator’s Licence. For vehicles over 7.5T, this is a legal requirement regardless of whether the goods are your own or carried for hire and reward. There are three main types of licence:
- Restricted: For transporting your own goods only
- Standard National: For goods transport within the UK
- Standard International: Required for international journeys
Operators must demonstrate financial standing, good repute, and professional competence via a qualified transport manager (or responsible person for a Restricted O Licence).
2. Vehicle Dimensions and Weights
All HGVs must comply with legal size and weight restrictions:
- Maximum gross vehicle weight: 44 tonnes (for artics with six axles)
- Maximum width: 2.55 metres (Dry Freight) 2.60 metres (Temperature Controlled)
- Maximum length: 16.5 metres (artics) or 18.75 metres (drawbars)
- Maximum length (LST): Under the latest STGO regulations, trailers up to 18.75 metres can be operated under certain conditions.
Axle loadings must also be within limits. Overloaded or overlength vehicles risk immediate fines and prohibition.
3. Driver Licensing
Drivers must hold the correct entitlement for HGV operation:
- Category C: For rigid HGVs over 7.5 tonnes
- Category C+E: For articulated vehicles or drawbars
Additionally, a Driver CPC card and digital tachograph card are required for legal operation.
4. Driver CPC
Professional HGV drivers must complete 35 hours of approved training every 5 years. This ensures drivers remain up to date on safety, legislation, and industry best practices. Failure to comply can result in fines and prohibition from driving professionally.
5. Drivers’ Hours & Tachograph Rules
Strict limits apply to how long drivers can work without rest. These are enforced via digital tachographs fitted to all modern HGVs:
- Daily limit: 9 hours driving (extendable to 10 hours twice per week)
- Weekly limit: 56 hours
- Fortnightly limit: 90 hours over any two weeks
- Breaks: 45 minutes after 4.5 hours driving (can be split 15 + 30)
- Rest: 11 hours daily (can reduce to 9 hours 3 times per week)
Smart tachographs are now mandatory for new vehicles used internationally.
6. Load Restraint and Security
All loads must be secured safely in accordance with current DVSA guidance. The aim is to prevent load movement under normal driving conditions such as braking, cornering or accelerating.
- Use suitable restraints: Straps, chains, headboards, or friction mats
- Prevent load shift: Loads must not slide, tip or roll
- Driver responsibility: Check load security before departure and during the journey
Unsafe loads are a leading cause of roadside prohibitions and can lead to fines or prosecution.
7. Vehicle Maintenance, Safety Inspections & Enforcement
Operators must ensure all HGVs remain roadworthy at all times. This is supported by structured maintenance schedules and enforced by DVSA roadside inspections.
Operator responsibilities:
- Daily walkaround checks: Carried out by the driver before use
- Planned maintenance: Typically every 6–13 weeks based on usage
- Annual MOT: Conducted at a DVSA-authorised test centre (ATF)
- Record keeping: Maintenance records must be retained for at least 15 months
DVSA enforcement:
- Brake testing: Roller brake tests assess performance and balance
- Component checks: Includes tyres, lights, suspension, and emissions
- Enforcement action: Prohibition notices (PG9), fines, or immobilisation if unsafe
Maintaining compliance protects your OCRS and avoids costly disruption.
8. Emission Standards & Clean Air Zones
Many UK cities now enforce Clean Air Zones (CAZ) or similar environmental schemes. Vehicles not meeting Euro 6 standards may incur daily charges in zones such as:
- London ULEZ/LEZ
- Birmingham
- Bristol, Portsmouth, Bradford, and others
Check vehicle compliance in advance or plan routes to avoid charges.
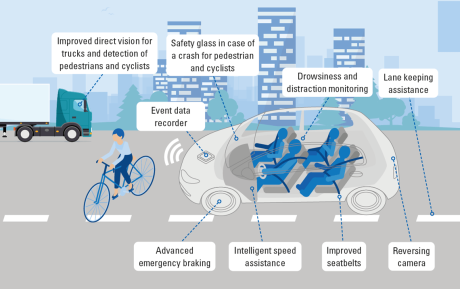
9. Direct Vision Standard (DVS)
HGVs over 12 tonnes entering Greater London must meet DVS requirements to improve driver visibility:
- Zero to 5-star rating: Based on direct line of sight from the cab
- Permit scheme: Zero-star vehicles require additional safety equipment
- Penalties: Up to £550 per vehicle per day for non-compliance
Updates to the scheme are being rolled out from 2024 onwards.
10. Road User Levy (Currently Suspended)
The HGV Levy applies to vehicles over 12 tonnes to contribute towards road wear and maintenance. While suspended since 2020, it is expected to return with revised emissions-based charges from 2026.
11. Health & Safety Obligations
Under the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974, operators must control risks related to vehicle use, especially during loading and unloading. This includes:
- Risk assessments for loading activities and yard movements
- Safe working procedures and equipment maintenance
- Training for drivers and yard staff handling vehicles
Accidents involving HGVs can result in serious legal and financial consequences. Prioritising safety is both a legal and moral obligation.
See related content below for more detailed guidance on each topic.
We’d love to hear from you – get in touch today!